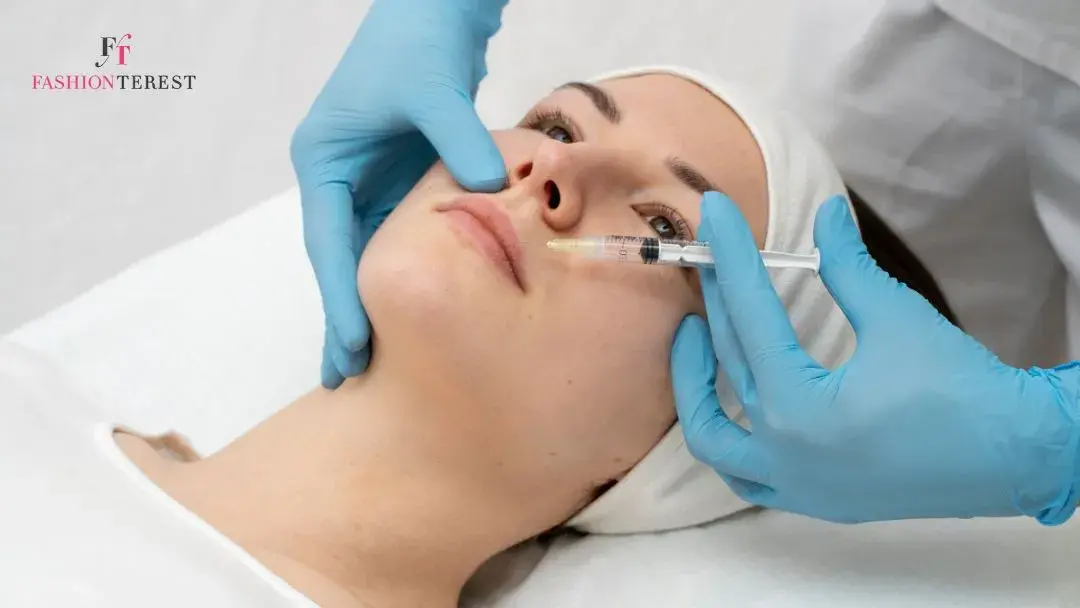
Hyperpigmentation occurs when the skin produces too much melanin, resulting in darker areas. It’s a common skin condition that affects people of all skin tones, although it may be more noticeable in people with darker skin. Understanding that hyperpigmentation can appear in various ways, from small localized spots to affecting the entire body, is critical for effective hyperpigmentation treatment.
Hyperpigmentation isn’t harmful in itself, but it can be a cosmetic concern for many people. Understanding its types, causes, and treatments is crucial in managing and treating it effectively.
Types of Hyperpigmentation

There are various types of hyperpigmentation, each with different causes and characteristics. Identifying the type of hyperpigmentation can help in determining the most effective treatment approach.
1. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
This type occurs after the skin has been injured or inflamed. It’s common after acne, burns, or other trauma to the skin, and it typically appears as flat, darkened patches. PIH can also develop after cosmetic procedures like chemical peels or laser treatments if the skin is irritated during the healing process.
2. Melasma
Melasma is a chronic skin condition that causes large patches of hyperpigmentation, usually on the face. It’s often triggered by hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy or when using birth control pills. This condition is more prevalent in women, though men can also develop melasma. Sun exposure can worsen melasma, making it more stubborn to treat.
3. Solar Lentigines (Sun Spots or Age Spots)
Solar lentigines are caused by prolonged exposure to the sun. They appear as flat, brown, or black spots, often on areas frequently exposed to the sun like the face, hands, and arms. Sun spots typically become more noticeable as a person ages, which is why they’re often referred to as age spots.
4. Freckles
Freckles are small, flat spots that can be red, tan, brown, or black. They usually become more prominent after sun exposure and are common in individuals with lighter skin tones. While freckles aren’t technically considered a form of hyperpigmentation caused by trauma or inflammation, they are a result of increased melanin production in response to UV exposure.
What Causes Hyperpigmentation?

Hyperpigmentation is primarily caused by an excess production of melanin, which is influenced by several factors:
1. Sun Exposure
UV radiation from the sun stimulates melanin production as a defence mechanism. Over time, repeated sun exposure can lead to dark patches or spots, such as sun spots, freckles, and other forms of hyperpigmentation.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, especially during pregnancy or from using birth control, can trigger hyperpigmentation, most commonly melasma. This is due to the increased sensitivity of melanocytes (melanin-producing cells) to hormones like oestrogen and progesterone.
3. Skin Injuries or Inflammation
As mentioned earlier, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) occurs when the skin heals from an injury or inflammation, like acne, eczema, or psoriasis. The skin responds by producing excess melanin, resulting in dark spots or patches.
4. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as Addison’s disease, can cause hyperpigmentation. Addison’s disease affects the adrenal glands, leading to an increase in melanin production. Other conditions that may result in skin darkening include hemochromatosis (iron overload) and acanthosis nigricans (a condition linked to insulin resistance).
5. Medications
Some medications, including certain antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and chemotherapy drugs, can cause hyperpigmentation as a side effect. The skin may darken as a response to the chemical components in the medications.
How to Get Rid of Hyperpigmentation

Treating hyperpigmentation can be a gradual process, and the effectiveness of treatments can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. There are various approaches to managing hyperpigmentation, ranging from topical treatments to professional procedures.
1. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are one of the most common ways to address hyperpigmentation. These products are often formulated with ingredients that lighten dark spots and even out skin tone. Some of the most effective ingredients for treating hyperpigmentation include:
Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent that inhibits melanin production. Hydroquinone is available both over-the-counter (in lower concentrations) and by prescription (in higher concentrations). It’s one of the most widely used treatments for hyperpigmentation but should be used under the guidance of a dermatologist to avoid side effects.
Vitamin C: Known for its brightening properties, vitamin C is an antioxidant that can help reduce melanin production and protect the skin from free radical damage. Regular use of vitamin C serums can help lighten dark spots over time.
Kojic Acid: Derived from fungi, kojic acid is another skin-lightening agent that works by inhibiting the production of melanin. It’s commonly found in skin-lightening creams and serums.
Azelaic Acid: This acid is particularly effective in treating post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially for those with acne-prone skin. It helps reduce melanin production and has anti-inflammatory properties.
Retinoids: Retinoids, including retinol and tretinoin, promote cell turnover and help fade dark spots by encouraging the shedding of pigmented skin cells. They also boost collagen production, improving skin texture and tone.
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs) and Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs): These exfoliating acids help remove dead skin cells, revealing brighter, more even-toned skin underneath. Glycolic acid (AHA) and salicylic acid (BHA) are commonly used to treat hyperpigmentation.
2. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels use a solution to remove the outer layer of skin, promoting cell turnover and revealing a rejuvenated appearance. Peels vary in strength, from superficial peels that only target the outermost layer of skin to deeper peels that penetrate multiple layers.
Chemical peels can be effective for treating different types of hyperpigmentation, including melasma and sun spots. However, they should be performed by a trained professional to minimise the risk of complications, especially for individuals with darker skin tones, who may be more prone to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
3. Laser Treatments
Laser treatments use concentrated beams of light to target and break down areas of hyperpigmentation. There are two main types of laser treatments for hyperpigmentation:
Ablative lasers: These lasers remove layers of skin, encouraging new skin growth. Ablative lasers are more aggressive and are usually reserved for more severe cases of hyperpigmentation.
Non-ablative lasers: These lasers target pigment in the skin without removing layers. Non-ablative lasers are generally less invasive and have a shorter recovery time compared to ablative lasers.
Laser treatments can be highly effective, but they may require multiple sessions for optimal results. It’s important to consult with a dermatologist or skin specialist to determine the best type of laser for your specific skin type and condition.
4. Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure that involves exfoliating the skin using a special device that sprays fine crystals or uses a diamond-tipped wand. This process removes the outer layer of skin, promoting the growth of new, more evenly pigmented skin cells.
Microdermabrasion is effective for treating milder forms of hyperpigmentation, such as sun spots or PIH. It may require several sessions to achieve noticeable results.
5. Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy
IPL therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses broad-spectrum light to target pigmented areas of the skin. It’s commonly used to treat sun spots and age spots but can also be effective for other forms of hyperpigmentation. IPL therapy is less aggressive than laser treatments, and it typically requires multiple sessions for the best results.
Home Remedies to Treat Hyperpigmentation

For those looking for natural alternatives or complementary treatments, there are several home remedies that may help lighten hyperpigmentation. While these remedies may not be as fast-acting or effective as professional treatments, they can offer mild improvement over time.
1. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera contains a natural substance called aloin, which can help lighten dark patches on the skin. Applying fresh aloe vera gel to dark spots may help reduce pigmentation over time. It also has soothing and healing properties, making it suitable for sensitive skin.
2. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar contains acetic acid, which helps lighten dark spots. To use it, mix equal parts apple cider vinegar and water and apply the mixture to the affected areas using a cotton ball. Leave it on for a few minutes before rinsing off. Be cautious with apple cider vinegar, as it can be irritating for some skin types.
3. Licorice Extract
Licorice extract contains glabridin, a compound that inhibits melanin production. It’s often found in natural skin-lightening products, but it can also be applied directly to the skin in its pure form to help fade dark spots.
4. Green Tea Extract
Green tea contains antioxidants that can help protect the skin from damage and reduce the appearance of dark spots. Green tea extract can be applied topically or used in DIY face masks to help brighten the skin.
5. Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that may help reduce pigmentation. You can make a turmeric paste by mixing turmeric powder with water or yoghurt and applying it to the affected areas. Leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off.
6. Vitamin E Oil
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that can help repair damaged skin and lighten dark spots. Applying vitamin E oil directly to the skin or mixing it with your moisturiser may improve the appearance of hyperpigmentation over time.
7. Milk or Yogurt
Lactic acid, found in milk and yoghurt, is a natural exfoliant that can help lighten dark spots and improve overall skin tone. You can apply yoghurt directly to your skin as a mask or use milk-soaked cotton pads to treat hyperpigmented areas.
Preventing Hyperpigmentation

Preventing hyperpigmentation is just as important as treating it. Here are some key tips to minimise the risk of developing new dark spots:
Sun protection: Wearing sunscreen with broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher is crucial for preventing sun-induced hyperpigmentation. Reapply every two hours, especially if you’re outdoors.
Avoid picking at your skin: Whether it’s acne, insect bites, or other skin irritations, avoid picking or scratching to prevent post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Use gentle skincare products: Harsh skincare products can irritate the skin and lead to hyperpigmentation. Choose gentle cleansers and moisturisers that won’t cause inflammation or damage.
Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain healthy skin and can promote faster healing of damaged areas.
Conclusion
Hyperpigmentation can be frustrating, but it’s treatable with the right approach. Whether you choose professional treatments or home remedies, consistency is key to achieving the best results. Consulting with a dermatologist will help tailor a treatment plan that fits your skin’s needs and addresses the root cause of your hyperpigmentation. With patience and proper care, your skin can regain its even tone and radiance.
In Case You Missed It!